Three-dimensional (3D) printing is a revolutionary technology that has transformed the way we produce objects. There are several different types of 3D printing techniques, but two of the most commonly used are Resin and Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM). Both of these techniques have unique advantages and disadvantages, and in this article, we will explore the differences between them.
Clicking on the Amazon Associate links in this article helps me pay the bills–and write more articles!
Resin 3D Printing
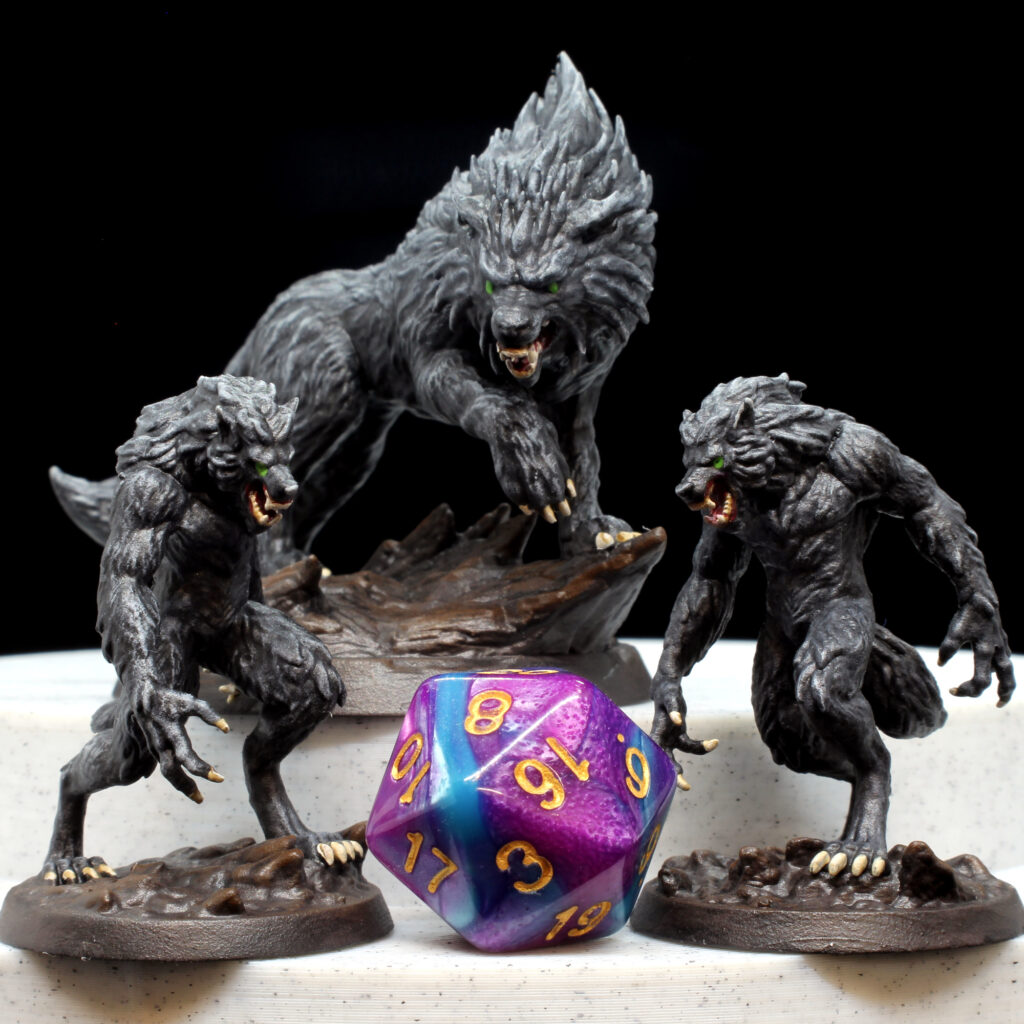
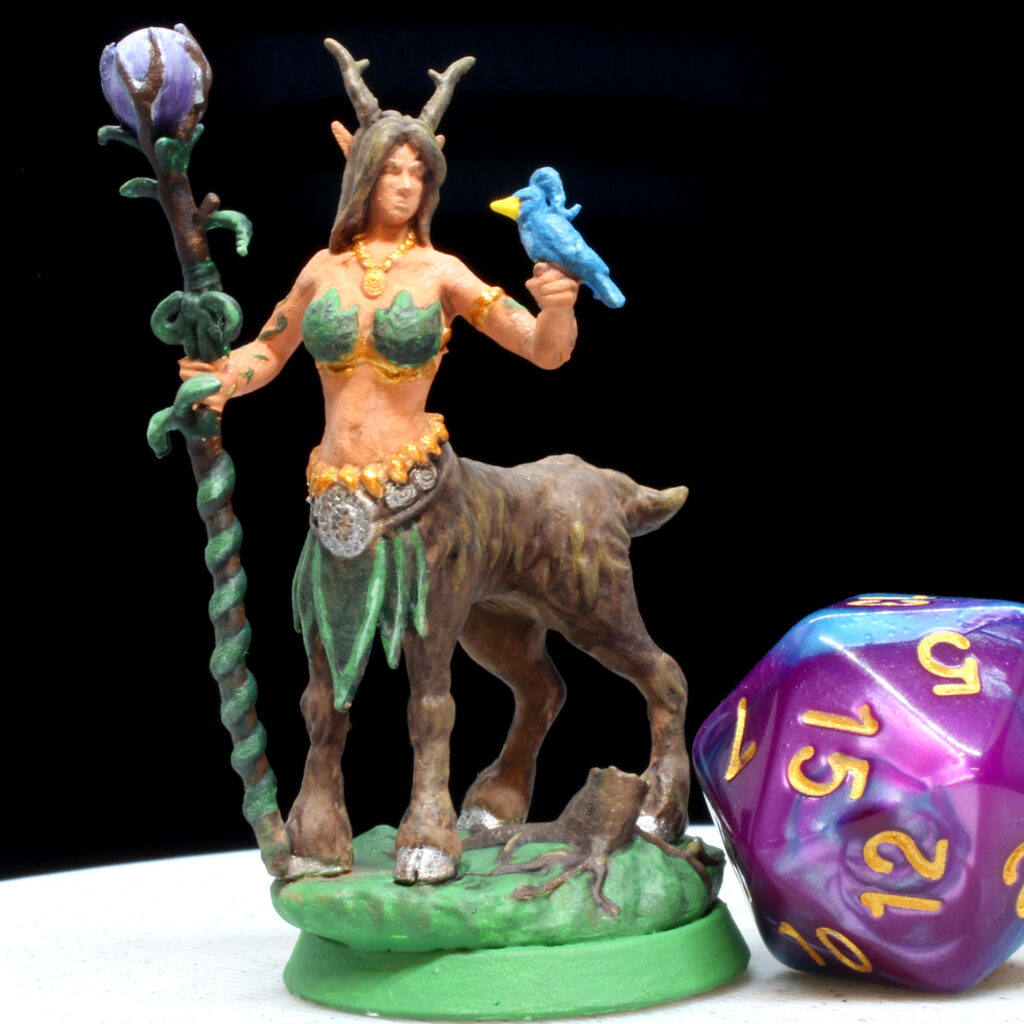
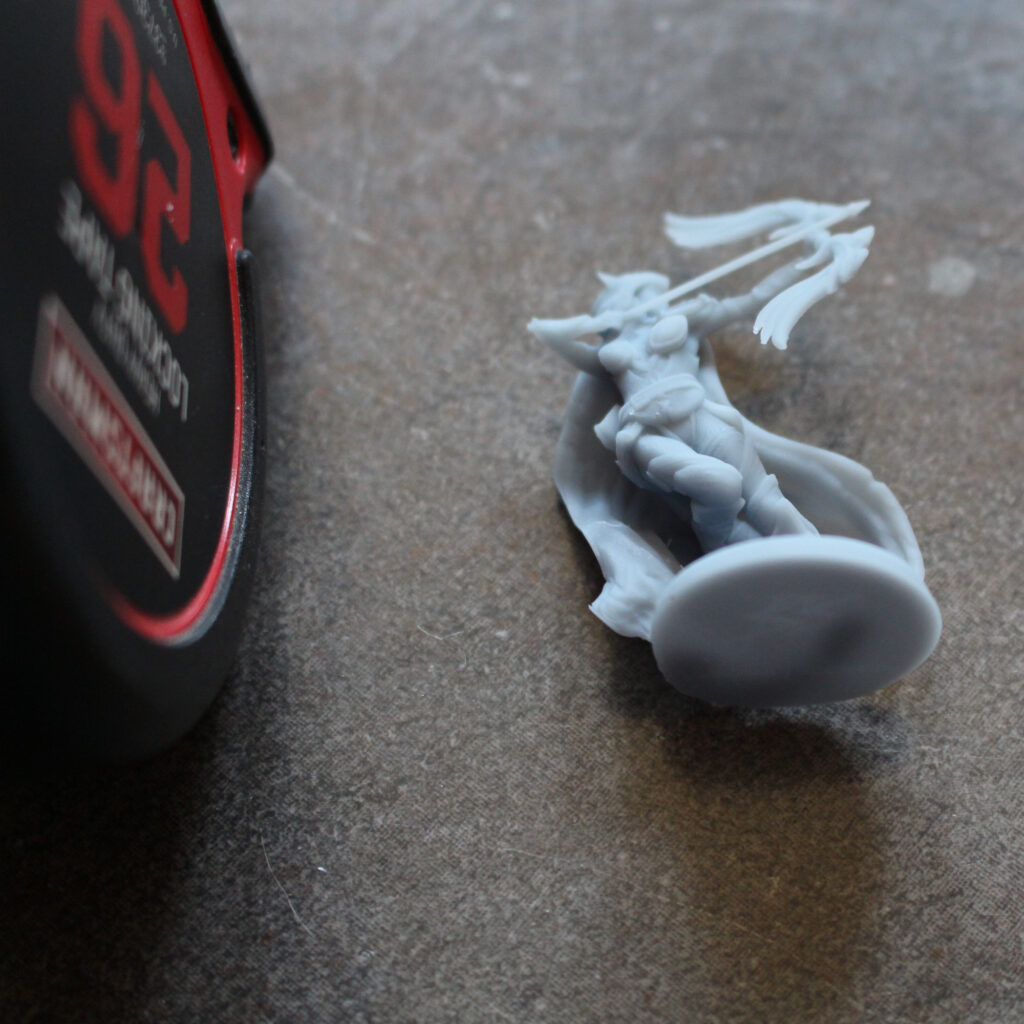
Resin 3D printing, also known as stereolithography (SLA) printing, involves using a liquid photopolymer resin that is cured (hardened) by a light source. This technique produces high-quality, detailed prints that are ideal for creating small or intricate objects. Resin 3D printing works by using a laser or projector to cure the resin in precise locations, layer by layer, until the entire object is complete.

Advantages of resin 3D printing:
- High level of detail: Resin 3D printing can produce incredibly detailed prints with smooth surfaces and intricate features.
- Large selection of materials: There are many different types of resin available, including flexible, clear, and high-temperature resistant resins.
- Minimal post-processing: Resin prints require minimal post-processing, as they do not have visible layers like FDM prints.
Disadvantages of resin 3D printing:
- Limited print size: The size of resin prints is limited by the size of the printer’s build platform.
- Messy and toxic: Resin 3D printing can be messy, as the liquid resin can spill and stain surfaces. Additionally, the chemicals used in the resin can be toxic and require careful handling.
- Longer print times: Resin 3D printing can take longer than FDM printing, as each layer must be cured individually.



Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) 3D Printing
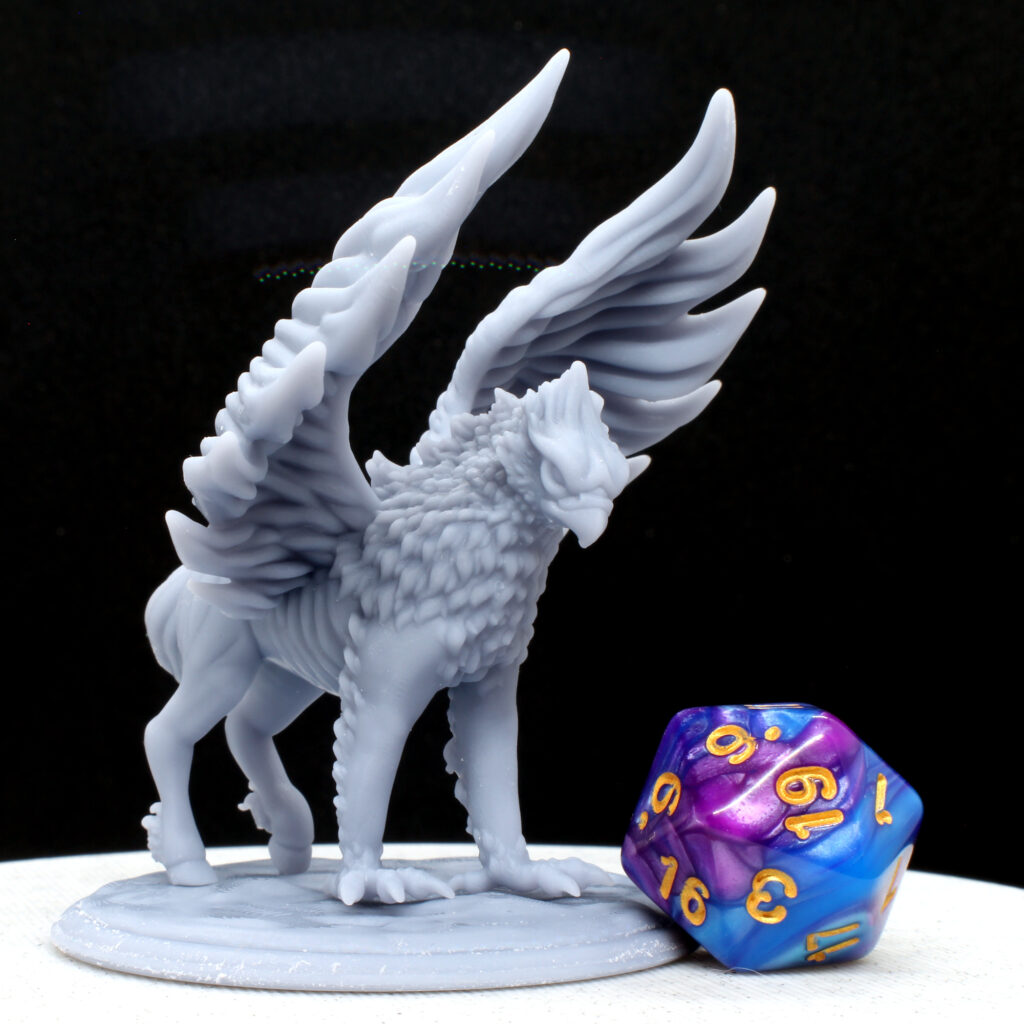
Fused deposition modeling (FDM) 3D printing is the most common type of 3D printing. It involves using a thermoplastic filament that is melted and extruded through a nozzle, layer by layer, until the entire object is complete. FDM 3D printing is a versatile and cost-effective method for creating large, functional objects.


Advantages of FDM 3D printing:
- Large print size: FDM 3D printing can create larger objects than resin 3D printing.
- Wide selection of filaments: There are many different types of filaments available, including PLA, ABS, and PETG.
- Fast print times: FDM 3D printing can create objects quickly, as multiple layers can be printed at once.
Disadvantages of FDM 3D printing:
- Visible layers: FDM prints have visible layers, which can require post-processing to smooth out.
- Limited detail: FDM prints can have less detail and precision than resin prints.
- Warping and cracking: FDM prints can be prone to warping or cracking, especially when printing large objects.



Conclusion
In summary, resin and FDM 3D printing have different strengths and weaknesses, and the choice of which method to use will depend on the desired application. Resin 3D printing is ideal for creating highly detailed, small objects, while FDM 3D printing is better suited for creating large, functional objects quickly and cost-effectively. Ultimately, both methods offer unique benefits, and the choice of which one to use will depend on the specific needs of the project.
Was this article helpful? Become a Patreon or buy me a coffee and I’ll write more!